GNSS vs GPS: What’s the Difference?

We occasionally get asked about the differences between GNSS and GPS.
Is there a difference, or are they basically the same? Are they related terms? Do I need a GPS repeater or a GNSS repeater?
This is a brief explanation of the relationship between GNSS and GPS.
GNSS – by definition ….
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System. This term describes a constellation of satellites providing signals from space that provide positioning and timing data to GNSS receivers down here on earth.
Satellite receivers use the positioning information to determine their location by calculating longitude, latitude and altitude from the received signals.
Additionally, each satellite provides a critical fourth dimension – time. Each satellite contains multiple atomic clocks that contribute very precise time data. GNSS receivers decode these signals, effectively synchronizing each receiver to the atomic clock signal.
There exists a number of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, usually owned and operated by separate countries or regions.
The first, and probably best known, is the Navstar Global Positioning System, generally referred to simply as “GPS”. It was developed by the United States Department of Defence (DoD). The system was initially intended for military use but was made available to civilian users.
The US-owned GPS is now the most widely used GNSS in the world, providing continuous timing and positioning data globally.
Global Positioning System (United States)
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Air Force.
It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to GPS receivers anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites.
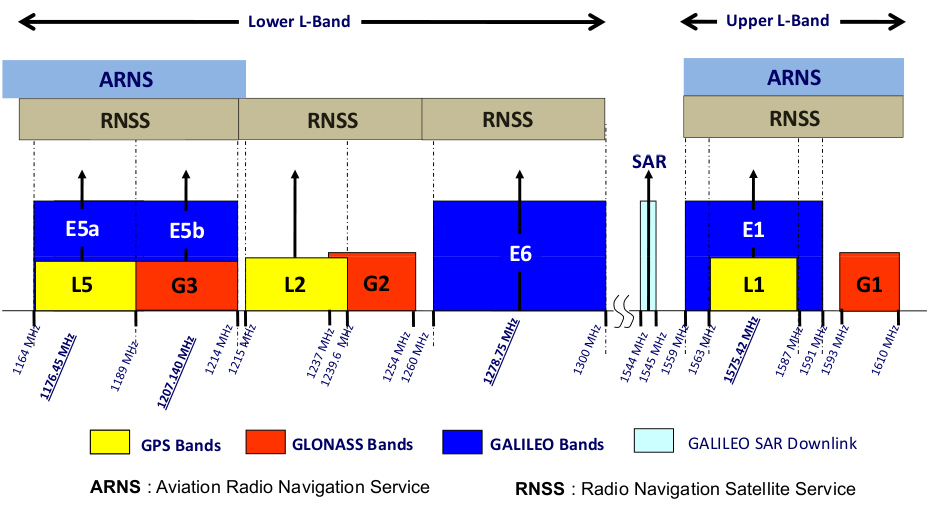
GPS L1 signal in upper L-band is centred around 1575 MHz.
GPS L2 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1227 MHz.
GPS L5 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1176 MHz.
Galileo (EU)
Galileo is the European Union’s GNSS constellation. It was created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA) and operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA). Galileo is available for civilian and commercial use. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European nations do not have to rely on the US GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time
Galileo E1 signal in upper L-band is centred around 1575 MHz.
Galileo E5 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1189 MHz.
Galileo E6 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1278 MHz.
GLONASS (Russia)
GLObal NAvigation Satellite System or GLONASS is a Russian satellite-based navigation system. It was the second navigational system to come into operation, providing global coverage with comparable precision to GPS.
GLONASS supplementation of GPS systems also improves positioning in high latitudes (north or south)
GLONASS G1 signal in upper L-band is centred around 1602 MHz.
GLONASS G2 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1246 MHz.
GLONASS G3 signal in lower L-band is centred around 1207 MHz.
BeiDou (China)
BeiDou is a Chinese-owned global satellite navigation system. Since June 2020 it has 35 operational satellites in orbit, in a constellation known as BeiDou-3 (third generation). Intended positional accuracy is 3.6m for the publicly-available service, with 10cm accuracy achievable with the encrypted service.
Summary
GPS is a type of GNSS. It was the first Global Navigation Satellite System to become available; hence the term “GPS” is often used to describe satellite navigation systems in general.
If a GPS repeater system is specified, it would cover the L1 band only. This repeater kit for L1 signals contains all parts needed to provide GPS signal inside a building where it would not normally be present.
The repeater kit for GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou strictly-speaking is a multi-GNSS system, but the term “GPS repeater” is used interchangeably.
A repeater kit for GPS L1, L2, GLONASS, Galileo and BeiDou is also a multi-GNSS system and covers all of the most commonly used signals available today.
FalTech has a range of GNSS/GPS repeater systems, plus Iridium repeaters and GNSS accessories such as inline amplifiers and signal splitters .
For more information please do get in touch.
Image source: European Space Agency